We are currently in Phase B3, analysing the data collected throughout the study period.
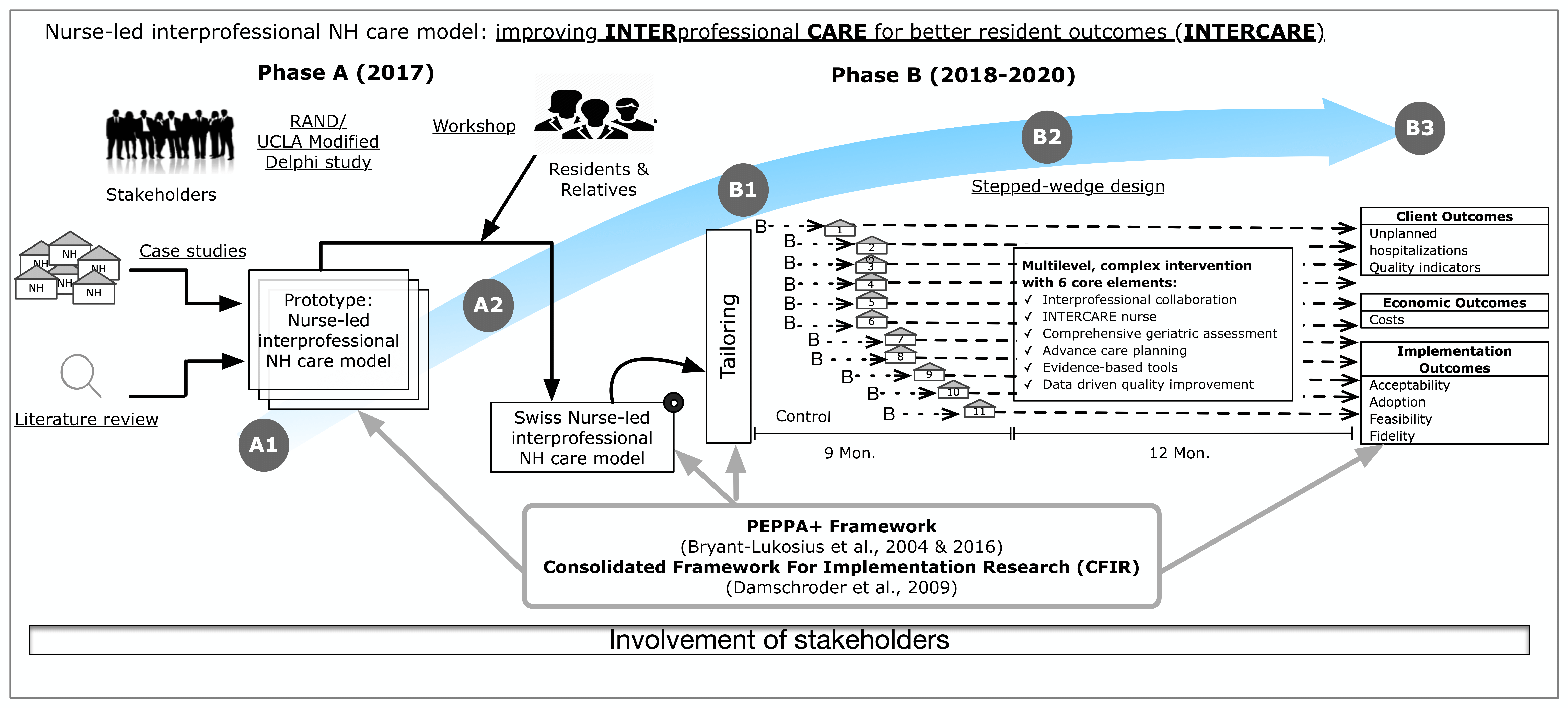
Phase A: Model Development
In phase A, a literature review and a descriptive analysis of national and international models of care already in place were carried out. With the participation of various stakeholders from nursing homes, nursing home associations, professional associations, APN representations, education, policy, insurance companies and patient representatives in Switzerland, the nurse-led model of care (INTERCARE nurse-led model of care) focusing on the reduction of avoidable hospitalizations was developed.
Phase B: Implementation and Evaluation
In phase B, the newly developed nurse-led model of care was introduced and is being evaluated in 11 nursing homes in German-speaking Switzerland, to provide a comprehensive picture of the impact of the nurse-led model of care. The data collection is finished.
Baseline Data Collection: the baseline data collection took place 3 months before the implementation phase, in all nursing homes and includes a survey of nursing home characteristics and a staff survey. Starting at baseline, quality indicators and hospitalizations were measured and are analyzed continuously. This allows each nursing home to serve first as a control and then as an intervention site.
Collection of evaluation data: the collection of evaluation data includes both questionnaire surveys and interviews, as well as specifically collected outcome data and routine resident data, e.g. the RAI-MDS. The leadership of the nursing homes, the care staff, physicians and the INTERCARE nurses will be repeatedly questioned about the new nurse-led model of care and its impact.
Data is collected at different levels:
1. Clinical Outcomes. These include unplanned hospitalizations as well as the four new measurement themes of the national quality indicators: pain, weight loss, polypharmacy and physical restraints.
2. Staff outcomes. We are interested in job satisfaction, the experience of empowerment and interprofessional cooperation during the implementation of the new nurse-led model of care.
3. Implementation outcomes. Measurement of acceptability, feasibility, degree of adoption, and fidelity to the new nurse-led model of care will be measured throughout the implementation phase.
4. Costs. We will assess how much the implementation of the new nurse-led model of care costs and how changes in hospitalization rates affect costs.